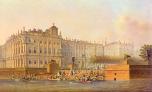hidden
|
Air Corps Aerodrome
AIR CORPS AERODROME, set up in 1910 in the south part of St. Petersburg, between Baltiiskaya and Varshavskaya Railway Lines, in the area of the present Blagodatnaya Street and Pobedy Street
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Airports (entry)
AIRPORTS (airdromes, terminal buildings). In 1911-14, in St. Petersburg’s first airport, Korpusnoy Airdrome was situated near present-day Novo-Izmailovsky Avenue (see Aviatorov Park)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Baltic Shipping Company
BALTIC SHIPPING COMPANY (BSC). The history of BSC (5 Mezhevoy Canal) goes back to the foundation of St. Petersburg-Lubeck Shipping Society in 1830; its present-day name was given in 1922. By 1941 BSC had 20 ships
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Baltiiskaya Pipeline System
BALTIISKAYA PIPELINE SYSTEM. A network of pipelines in the Northwestern Federal District of Russia, intended to transport petroleum and crude oil from the Komi Republic and Western Siberia for export and to meet the region's needs
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Baltiysky Railway Station
BALTIYSKY RAILWAY STATION (120 Obvodny Canal Embankment). The station was built in 1853 after a railway between St. Petersburg and Peterhof was completed, and was originally called Peterhofsky Railway Station. Architect A.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bus
BUS, the most mobile type of city public transport, provides cost-effective route planning and is extremely flexible to changes in the route network. The first attempt to organize "motorized omnibus" service goes back to the 1880s
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bus Depots
BUS DEPOTS, enterprises providing for parking, technical maintenance, and repair of buses. They consist of a roofed depot building, vehicle technical maintenance facilities, and an administrative office
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bus terminals
BUS TERMINALS are bus stations for intercity and international bus passenger transit. The first bus terminal (No 1) was opened in 1955 at 37 Sadovaya Street in the building of the former Sennoy Market guardhouse (architect V.I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Cabmen
CABMEN, appeared in St. Petersburg in the city's early days (decree of 1705 "On Taxing Cabmen"), at about the same time cab driving grew into a business practised as a rule by peasants. By 1745 there were 3,000 cabmen in St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
City transport (general article)
CITY TRANSPORT, transport means for intra-city freight and passenger transportation, as well as transport, providing public services. City transport is divided into passenger, freight and special urban transport
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Finlyandsky Railway Station
FINLYANDSKY RAILWAY STATION (5 Lenina Square), was built in 1870 by architect P.S. Kupinsky. It was a single-story building with a 2-storied pavilion. The side facade with the pavilion for the members of the Imperial Family was accessed via the
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Horse-car
HORSE-CAR (horse-railway; horse-tram), a railway type of omnibus. In the second half of the 19th - early 20th century horse-cars were the most available passenger public transport means
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Komendantsky Aerodrome
KOMENDANTSKY AERODROME, an area in the north-west of St. Petersburg, between Kolomyazhsky Avenue, Parashyutnaya Street, Sizova Street and Chernaya Rechka river
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Krasnaya Strela High-class Service Train
KRASNAYA STRELA high-class service train is the first high-class service train in the Russian railway system, travelling along Oktyabrskaya Railway between Moscow and St. Petersburg (Route #1 from St. Petersburg, and Route #2 from Moscow)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ladoga Pipeline
LADOGA PIPELINE, a trunk pipeline laid in 43 days (5 May - 16 June 1942), through Lake Ladoga from Karedzhi Cape to the Borisova Griva Railway Station, in order to supply Leningrad with oil during the Siege of 1941-44. Designed by engineer N. V
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Landings, Water (entry)
LANDINGS, WATER. Ship landings were present in St. Petersburg from the first years of its existence. Their location depended on the location and orientation of storage warehouses
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Moskovsky Railway Station
MOSKOVSKY RAILWAY STATION (in 1855-1924 Nikolaevsky Railway Station) (located at 2 Vosstaniya Square), was built in 1844-51 by architect K.A. Ton. A commemorative plaque in his memory appears on the facade
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Northwest Shipping Lines
NORTHWEST SHIPPING LINES (NWS) (the central office is located at 37 Bolshaya Morskaya Street), open joint-stock company (since 1991), one of the largest enterprises of St. Petersburg transport sector and the system of Russian river transport
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Oktyabrskaya Railway
OKTYABRSKAYA RAILWAY runs across Leningrad, Vologda, Moscow, Murmansk, Novgorod, Pskov, and Tver Regions and the Republic of Karelia. The total length of the network is 10.4 thousand km. The company office is located in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Omnibus
OMNIBUS (lat. omnibus - for all), a multi-seater horse-powered vehicle, the first public city route of trackless transportation. First omnibuses started operating in the summer of 1830, running from St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
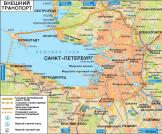
Petersburg Transportation Hub
PETERSBURG TRANSPORTATION HUB. European Russia's largest transport centre. St. Petersburg's unique geographical location, with its accessibility to sea, river and railway routes, as well as major highways
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Railway Stations (entry)
RAILWAY STATIONS (Russian 'vokzal', from English 'vauxhall', after the name of J. Vaux, owner of an amusement hall near London in the 18th century). In Russian the word 'vokzal' traditionally refers to the terminal station of the first Russian
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
River Passages
RIVER PASSAGES. Ever since the early years of St. Petersburg's existence, river passages were set across the Neva river and its canals to provide communication between the islands, by water means of transport in summer and on the ice in winter
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
River Port
RIVER PORT (195 Obukhovskoy Oborony Avenue) was put in operation in 1970 (designed by architects I.N. Kuskov and V.V. Popov). The port was built on the site of the former Ozernaya Quay. The port was intended for passenger transportation
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sea Passenger Terminal
SEA PASSENGER TERMINAL (located at 1 Morskoy Slavy Sq.), is a closed joint-stock holding company, dealing with freight and passenger transportation between St. Petersburg and Germany, travel services and hotel business
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sea Port
SEA PORT, Merchant (located at 5 Mezhevoy Canal) is one of the oldest merchant seaports of Russia, and the biggest operator of cargo traffic in St. Petersburg Sea Port. The first port buildings were laid in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Steam Railway
STEAM RAILWAY (horse-drawn railway, steam-driven tram). Urban transport, a type of horse-drawn tram. Steam traction was introduced in 1882 along the Nevskaya Horse-Drawn Railway on the route from Znamenskaya Square (today Vosstania Square) to
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
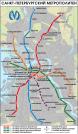
Subway
SUBWAY. First subway projects in St. Petersburg date back to the late 19th century. In 1889 the Administrative Committee of the Baltic Railway came up with a project of a subway line connecting Baltiysky and Finlyandsky Railway Stations
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Taxi
TAXI (borrowed into Russian from the word derived from English tax), motor vehicles transporting passengers for a fee. Private taxicabs appeared in St. Petersburg in the autumn of 1908, at the same time carrier joint-stock companies sprang up
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tram Depots
TRAM DEPOTS, enterprises providing special facilities and equipment for parking, maintenance and repair of tramway cars. The first Tram Depot (Petersburg Tram Depot
|
|
|
|
|