Persons
/
Peter I, Emperor
hidden
|
Dutch
DUTCH, an ethnic community within the St. Petersburg population. The Dutch language is related to the Germanic group of Indo-European languages. They are Protestant and Catholic (those living in St. Petersburg are mostly Protestant)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Earthern Dams
EARTHERN DAMS, zones within the territory of St. Petersburg with an artificially raised level. From the very first days of the city development bedding was used for the low spots to protect it from water, especially floods
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ekaterinhof
EKATERINHOF, a country estate. Tsar Peter the Great presented it to his wife Ekaterina Alexeevna (the future Empress Catherine I) in 1711. It was situated on Ekaterinhofsky Island
|
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
hidden
|
Elizaveta (Elizabeth) Petrovna (1709-1761), Empress
ELIZAVETA (Elizabeth) PETROVNA (1709-1761, St. Petersburg), Empress (since 1741), daughter of Peter the Great and Elizaveta I. Before taking the throne, she lived in a palace at the Tsaritsyn Medow in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Eropkin P.M. (about 1698-1740), architect.
EROPKIN Peter Mikhailovich (about 1698-1740, St. Petersburg), architect, urban planner, architecture theorist. In 1716-24 on the order of the Tsar Peter the Great he was trained in Italy, in 1725 he was conferred a title of architect
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Falconet E. M., (1716-1791), sculptor
FALCONET Etienne Maurice (1716-1791), sculptor. He studied sculpture under J. B. Le Moin in Paris in 1734-44. He was the director of the Sevres Porcelain Factory in 1757-66
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Felten Y. M. (1730-1801), architect
FELTEN Yury Matveevich (Georg Friedrich) (1730 -1801, St. Petersburg), architect, professor of the Academy of Fine Arts (from 1775; from 1785 a Council member, in 1789-94 director), State Counsellor (1784)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Feofan (Feofan Prokopovich (1681-1736), statesman and church figure, writer
FEOFAN/THEOPHAN (lay name Eleazar Prokopovich) (1681-1736, St. Petersburg), church figure. He studied at Kiev Theological Academy (until 1698), then at colleges of Vladimir-Volynsky
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Field of Mars (Marsovo Pole), ensemble
FIELD OF MARS (in the 18th century Bolshoy Meadow, Poteshnoe Field, Tsaritsyn Meadow, in 1918 -40 – Zhertv Revolyutsii Square), the square in the centre of St. Petersburg. It was named so in honour of Mars, the Roman god of war
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fireworks
FIREWORKS (in the 18th century - poteshnye ogni, toy-lights). The tradition of lighting firecrackers on holidays in St. Petersburg was introduced by Peter I. Fireworks were usually combined with illumination - luminous scenery (allegories)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fontanka, river
FONTANKA (known as Bezymyanny Erik until 1712-14), river, a branch in the Neva river delta, which crosses the central part of the city. The river flows from the Neva on the left, beside the Summer Garden
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Foreigners in St. Petersburg (entry)
FOREIGNERS, from the 18th to the early 20th century, foreigners were an important element of the St. Petersburg population. Foreigners appeared in the city from the moment of its foundation
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Founding of St. Petersburg
FOUNDING OF ST. PETERSBURG. In May 1703, after the surrender of Nyenschantz, Tsar Peter the Great decided to build a fortress at the mouth of the Neva River on Zayachy Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Funeral Rites (entry)
FUNERAL RITES. Burials during the building of St. Petersburg were noted for their utmost simplicity. As C. Weber (1718) witnessed, "a body wrapped in a coarse bast sack, tightened with ropes, and put on a bier
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gannibal (Hannibal) А.P. (1697-1781), engineer, general
GANNIBAL Abram (Ibrahim) Petrovich (around 1696-1781, of Suyda Sofiysky District, St. Petersburg Province), Peter the Great's godson, military engineer, chief engineer (1756), Major-General (1759), great-grandfather of Аlexander Pushkin
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gatchina, town
GATCHINA (in 1923-1927 Trotsk, in 1927-1944 Krasnogvardeisk), a town in Leningrad Region, 45 km to the south from St. Petersburg. Known since 1499 as Khotchino village, since the early 18th century - the Gatchinskaya farm-stead
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
General Plans for the Development of Petersburg-Leningrad
GENERAL PLANS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF PETERSBURG-LENINGRAD. One the first projects of St. Petersburg planning dates back to 1709-12. According to it, the city centre should be situated at Kotlin Island and was to be connected to outer parts of the
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Germans
GERMANS, an ethnic community forming a part of the St. Petersburg population. German language is related to the Germanic group of Indo-European languages. Their religion is Lutheran (amongst the St. Petersburg population up to 90%) and Catholic
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Glinka Capella
THE GLINKA CAPELLA (Leningrad Academic Glinka Capella), 20 Moika River Embankment, the oldest professional choir. It takes its origin in the Choir of Sovereign’s Chorister Scribes established in Moscow in 1479 for singing at church services and
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Golovkin G.I. (1660-1734), count, statesman
GOLOVKIN Gavriil Ivanovich (1660-1734, St. Petersburg), Count of the Holy Roman Empire (1707), Count of the Russian Empire (1709), diplomat, statesman, associate of Emperor Peter the Great (half-cousin of Tsarina Natalia Kirillovna, nee Naryshkina
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gottorp Globe
GOTTORP GLOBE, a unique planetarium globe - a hollow rotating sphere over 3.1 metres in diameter with the Earth surface pictured on the outside and a celestial map on the inside of the sphere
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Great Northern War of 1700-21
GREAT NORTHERN WAR OF 1700-21 was the war declared by a coalition of states from Central and Eastern Europe (the main participants were Russia, Denmark and Saxony) against Sweden
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Grilles (entry)
GRILLES. St. Petersburg boasts a number of unique metal grilles, created in the course of three centuries. Wrought grilles of bars with (sometimes gilded) decorative figures made from flat iron bars (the grille of the Ekaterininsky (Catherine)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Guards
GUARDS, life guards, elite, privileged military unit. The Russian Guards were established by Peter I in 1700, when the Preobrazhensky and Semenovsky regiments gained the title of life guards
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gymnasia (entry)
GYMNASIA, institutions of intermediate general education. In pre-revolutionary Russia they were mainly established with the purpose of training pupils for university and service in state institutions
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gypsy Choruses (entry)
GYPSY CHORUSES, up to the early 20th century they were called "Moscow Gypsy Choruses" (that is, Russian) in contrast to Hungarian, Spanish, Crimean. Practically all soloists had stage names, their real names having been for the most part lost
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Handicraft (overview)
HANDICRAFT, an important part of St. Petersburg economy in the 18th to the early 20th centuries, started developing soon after the city was founded as craftsmen were coming here from various handicraft centres of the country
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Head Magistrate
HEAD MAGISTRATE, the public institution of the highest rank. It was established in St. Petersburg on the decree of tsar Peter the Great in 1720 to function as the principal establishment in charge of city magistrates of other cities and towns. In St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Hermitage Buildings (entry)
HERMITAGE BUILDINGS. Hermitages were compulsory for all large court estates such as Peterhof and Tsarskoe Selo built as detached pavilions for confidential meetings from the early 18th century
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Hermitage Theatre
HERMITAGE THEATRE at 32 Dvortsovaya Embankment is a monument of 18th century architecture, is part of the complex of Hermitage buildings. It is the only 18th century theatre hall preserved in St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Hessen A.E. (1917- 2001 ), architect-restorer
Hessen Alexander Ernestovich (1917, Petrograd - 2001, St. Petersburg), architect, restorer, one of the founders of the school of scientific architectural restoration in Leningrad. He graduated from the Academy of Fine Arts (1939)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Highest Organs of State Power (entry)
HIGHEST ORGANS OF STATE POWER. The first higher organ of state power to function in St. Petersburg was the Senate founded by Tsar Peter the Great in 1711. The Supreme Privy Council was founded under Empress Catherine I (1725-30)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
His Imperial Majesty's Cabinet
HIS IMPERIAL MAJESTY'S CABINET, central state institution. Created in 1704 as Tsar Peter the Great's private cabinet, conducting the personal correspondence of Russian Emperors, managing their personal finances and property
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Holy Trinity and St Peter's Cathedral
HOLY TRINITY AND ST PETER'S CATHEDRAL, located at Troitskaya Square. An 18th century architectural monument. The first wooden church on this place was built in 1709-11, by order of Tsar Peter the Great
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Hospitals (common)
HOSPITALS. The first hospital in St. Petersburg, the Kalinkinsky Hospital was founded as a police-correctional institution for "indecent women and girls" (1762)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Hospitals, military (common)
HOSPITALS, MILITARY. The first Admiralty hospital was set up by order of Tsar Peter the Great on Vyborgskaya Side in 1715. In 1717, the Land military hospital was opened, which together with the Admiralty hospital formed a single ensemble (the 1720s
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Hydrometeorological Monitoring
HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL MONITORING. Visual weather and Neva level monitoring conducted ever since St. Petersburg was founded as decreed by Peter the Great. Regular hydrometeorological monitoring started for the first time in Russia in 1722. F. C
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ignatiev P.N. governor-general in 1854-61
IGNATIEV Pavel Nikolaevich (1797-1879, St. Petersburg), count (1877), statesman, infantry general (1859), adjutant-general (1846), honorary member of St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1856)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Imperial Burial Vault
IMPERIAL BURIAL VAULT. A final burial place for members of the Imperial Family had not yet been ultimately determined during Peter the Great's reign. The Tsars' kin were most often buried at the Holy Annunciation Church Burial Vault
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Imperial Court
IMPERIAL COURT, Russian Emperors' court personnel, organized by Emperor Peter the Great according to French and Prussian courts, finally brought under strict regulations during Emperor Nikolas I's reign
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Imperial Funerals
IMPERIAL FUNERALS, one of the most important ceremonies. Performed according to Emperor Peter the Great's funeral (1725), consisting of three parts: display of the body of the departed, transportation of the body to the SS
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Imperial Residences
IMPERIAL RESIDENCES, palaces, the official abodes of the Emperors, the Imperial Court, recognized by law as such; property of the Treasury and maintained at the expense of the State Treasury House. The place of court ceremonies
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ivan VI Antonovich (1740-1764), Emperor
IVAN VI (1740, St. Petersburg — 1764, Schlisselburg Fortress), Emperor (1740-1741). He was the son of Anna Leopoldovna and Prince Antony Ulrich of Brunswick, grandson of Tsar Ivan V (brother of Peter the Great)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Izhora Plants
IZHORA PLANTS (1 Lenina Avenue, Kolpino), an open joint-stock company, which was founded in 1992. It originated from the Menshikov Izhora Sawmill, built in the early 18th century at the Izhora River
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Jews
JEWS, an ethnic community within the St. Petersburg population. Hebrew is related to the Semitic group of Afrasian languages, Yiddish (was spread throughout the majority of eastern Russia) is related to the Germanic group of Indo-European family of
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kantemir A.D. (1708-1744), poet
KANTEMIR Antiokh Dmitrievich (1709-1744), Prince, poet, translator, diplomat, privy counsellor (1741). The son of a Moldavian Hospodar (Prince) D. K. Kantemir. He received an excellent home education, studied at the Academic University (1726-27)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kikiny Palaty (Kikin's Chambers)
KIKINY PALATY (Kikin's Chambers) (9 Stavropolskaya Street), an architectural monument of the Petrine Baroque. Constructed in 1714-20 (architect A. Schluter) for the Admiralty Councillor A.V
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
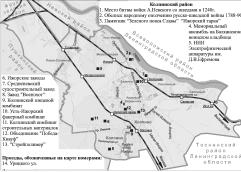
Kolpinsky District
KOLPINSKY DISTRICT, an administrative and territorial unit of Saint Petersburg (with the territorial administration situated in Kolpino, at 1 Uritskogo Street). The name derives from the town of Kolpino which is the centre of the district
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Korobov I.K. (1701-1747), architect
KOROBOV Ivan Kuzmich (1700 or 1701-1747), architect and engineer, a representative of Petrine Baroque. He studied in Holland and Belgium as a retainer of Peter the Great (1718-1727). After he returned to St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Korotkov N. S. (1874-1920), surgeon
KOROTKOV Nikolay Sergeevich (1874-1920, Petersburg), surgeon, Doctor of Medicine (1910). He graduated from Moscow University (1898). Korotkov moved to St. Petersburg in 1903
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Krasnoe Selo, area
KRASNOE SELO, a town; since 1973, it formed a part of Krasnoselsky District of Leningrad; since 1997 - municipal unit; 26 km to the south-west of St. Petersburg centre, on Narva federal motorway. A railway station on the line St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Krasny Kabachok, tavern
KRASNY KABACHOK ("Red Pub"). A tavern located on the 7th Verst of Petergofskaya Road. Named after Krasnenkaya Road, it was located at the building constructed for Tsar Peter I in the early 18th century as a rest-stop on his way to Strelna and
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Krestovsky Island
KRESTOVSKY ISLAND (Cross Island), situated between the Srednaya Nevka River separating it from Elagin Island, the Malaya Nevka River separating it from Petrovsky Island, Petrogradsky Island, Aptekarsky Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kronschlot
KRONSCHLOT, a sea fort, the first fortification of the Kronstadt Fortress. It was founded in the winter of 1703-04 on a shallow in the Gulf of Finland, south of Kotlin Island based on the designs of Tsar Peter the Great
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
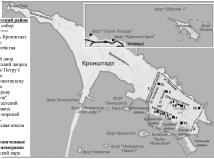
Kronstadt
KRONSTADT, a town on Kotlin Island, 32 kilometres west of Saint Petersburg. The town's history traces back to a sea fort called Kronslot built in the winter of 1703-04. By May 1704, two batteries were constructed along the south bank
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kronstadt Fortress
KRONSTADT FORTRESS (Kronstadt, 1 Yakornaya Square), museum, a branch of the Central Military and Naval Museum. Organised by A. A. Antipov who also acted as its first director the museum was opened on 8.5.1980 in the building of the Naval Cathedral
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kronstadt Fortress
KRONSTADT FORTRESS, a complex of fortifications supported by Kotlin Island, intended to defend St. Petersburg from the enemy naval attacks from the Gulf of Finland, the largest naval construction in the pre-revolutionary Russia
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kronstadtsky District
KRONSTADTSKY DISTRICT is an administrative territorial unit of St. Petersburg (Its territory administration is located at 36 Lenina Avenue,.) Formed in 1998, it was named after the city of Kronstadt, which is the district centre
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kunstkammer
KUNSTKAMMER (from German "Kunstkammer" - "chambers of curiosities, museum") (3 Universitetskaya Embankment). The oldest museum in Russia, was founded in 1714 based on the private collections of Peter the Great
|
|
|
|
|