Persons
/
Catherine II, Empress
hidden
|
Kokorinov A.F. (1726-1772), architect
KOKORINOV Alexander Filippovich (1726-1772, St. Petersburg), architect and engineer. He was one of the first masters of Russian Classicism. He studied in Tobolsk and Moscow. Kokorinov lived in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Krasny Kabachok, tavern
KRASNY KABACHOK ("Red Pub"). A tavern located on the 7th Verst of Petergofskaya Road. Named after Krasnenkaya Road, it was located at the building constructed for Tsar Peter I in the early 18th century as a rest-stop on his way to Strelna and
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kulibin I.P., (1735-1818), mechanic and inventor
KULIBIN Ivan Petrovich (1735-1818), self-taught mechanic and inventor. In 1764-67, he created a watch with a complicated mechanism in the shape of an egg. After presenting the watch to Empress Catherine II in 1769 (the watch is now part of the State
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kushelevka, area
KUSHELEVKA, an area in Vyborgskaya Side, between Karbysheva Street, Nepokorennykh Avenue, Bogoslovskoe Cemetery and Polyustrovsky Avenue. In 1781, Empress Catherine II granted 746 desyatin of land "in Vyborgskaya Side between Pargolova Dacha
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lakhta, locality
LAKHTA, a landmark northwest of Saint Petersburg, on the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland, in the vicinity of a cognominal railway station and Lake Lakhta; neighbours Olgino on the West, and Staraya Derevnya on the East
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Libraries (entry)
LIBRARIES. The first library of St. Petersburg was founded in 1714 by the decree of Tsar Peter the Great as His Majesty’s Library; later on, it formed the basis of the Library of the Russian Academy of Sciences
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Literary journals (entry)
LITERARY JOURNALS. The genesis of the Russian literary journalism is associated with St. Petersburg, where in 1728-36 and 1738-42 circulated first and only journal in the Russian language at that time - Primechaniya k Vedomostyam (the name changed)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lomonosov Porcelain Factory
LOMONOSOV PORCELAIN FACTORY (LPF) (151 Obukhovskoy Oborony Anevue) is the largest porcelain factory in the country, leading manufacturer of decorative porcelain. The factory was established in 1744 as the Portselinovaya Manufactory
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Marble Palace
MARBLE PALACE (1/5 Millionnaya Street), an architectural monument of early Neoclassicism. It was constructed in 1768-1785 (architect A. Rinaldi) for Count G.G. Orlov, a favourite of Empress Catherine II
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Maria Fedorovna, (1759-1828), Empress
MARIA FEDOROVNA (1759-1828, St. Petersburg), Empress (from 1796). Nee Sophie Dorothea Auguste Louise, Princess of Wurttemberg. She was Emperor Pavel I's second wife (from 1776)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Masonic Lodges
MASONIC LODGES, associations (meetings) of the followers of the religious-ethical doctrine (masonry), urging people to unite on the principles of equality, mutual aid and fraternal love
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Menagerie (an ensemble of the Alexander Park)
The oldest part of the park, founded as the Menagerie, occupied more than a half of the Alexander Park territory. The area for the Menagerie has been chosen as early as 1710
|
|
|
Source: Tsarskoe Selo
|
|
hidden
|
Mikeshin M.O., (1835-1896), artist
MIKESHIN Mikhail Osipovich (1835-1896, St. Petersburg), painter, graphic artist, sculptor. Studied at the Academy of Arts (1851-58), became a member in 1869. Won a competition in 1859 for the monument for the Millennium of Russia in Novgorod the
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mining Museum
MINING MUSEUM of the St. Petersburg State Mining Institute, at 2 Twenty-First Line of Vasilievsky Island, is one of the oldest and biggest geological museums in the world
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mirovich V. Y. (1740-1764), podporuchik
MIROVICH Vasily Yakovlevich (1740-1764, St. Petersburg), a podporuchik (sub-lieutenant) of the Smolenksky Infantry Regiment who did his military service in the garrison of Shliesselburg Fortress where ex-Emperor Ioann VI had been kept as a secret
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Monumental Propoganda Plan (monuments)
MONUMENTAL PROPAGANDA PLAN was ratified on 12 April 1918 by the Council of People's Commissars decree on the "removal of monuments, erected in honour of tsars and their servants and the elaboration of monuments of Russian Socialist Revolution" (On
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Munnich B. K. (1683-1767), Engineer, Governor General 1728-34
MUNNICH Christofor Antonovich (Burchard Kristoff) (1683-1767, St. Petersburg), Count (1728), statesman and military figure, General Field Marshal (1732). He was German by birth, came to Russian service in 1721
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Music Publishing Business
MUSIC PUBLISHING BUSINESS. Printed music was more expensive than handwritten in the 18th century to the first halа of the 19th century. Initially it was only printed for special occasions, later - only for a small number of followers
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Nativity of St. John the Baptist Church
NATIVITY OF ST. JOHN THE BAPTIST CHURCH, located at 7 Kamennoostrovsky Avenue. An architectural monument, built on Kamenny Island in 1776-78. The construction of a red brick church in Neo-Gothic style by architect Y. M
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Naval monuments
NAVAL MONUMENTS. St. Petersburg is the cradle of the Russian Navy, which explains the large number of monuments related to the history and eminent naval figures, beginning with its founder Peter the Great. The Boat House in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Neoclassicism
NEOCLASSICISM (from the Latin сlassicus - exemplary), the style in art and architecture, based on the cult of reason and ideal order, the antique heritage being its source
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Novikov N.I. (1744-1818), journalist, publisher
NOVIKOV Nikolaiy Ivanovich (1744-1818), man of letters, journalist, publisher. Studied in the gymnasium affiliated to the Moscow University (1756-59). From 1762-67 and 1769-79 lived in St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Old Believers
OLD BELIEVERS, a sect within the Orthodox Church consisting of those people who rejected the reforms of Patriarch Nikon in the middle of the 17th century and preserved the "old" ceremonies and traditions. Old Believers began settling in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Opekushin A.M., (1838-1923), sculptor
Opekushin Alexander Mikhailovich (1838-1923), sculptor. Studied at the Drawing School of the Society of Art Promotion and in the workshop of sculptor D.I. Jensen. Was a full member of Academy of Arts (1895)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Oranienbaum, palace and park ensemble
ORANIENBAUM, a palace and park ensemble (Lomonosov town) that started to form during the first quarter of the 18th century, when the country estate of A.D. Menshikov appeared on the coast of the Gulf of Finland 44 kilometres from St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Orlov Family
ORLOV FAMILY, nobles, counts and princes, known since the 17th century. Brothers Grigory, Vladimir, Alexey and Fedor Orlov took an active part in the take-over of 28 June 1762
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ostrovskogo Square
OSTROVSKOGO SQUARE known as Alexandrinskaya Square before 1923, between Nevsky Prospect and Zodchego Rossi Street. It was renamed after playwright A. N. Ostrovsky (1823-86). The square was designed by architect K. I
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Palace Coups (entry)
PALACE COUPS is a term used for coups of the state from the 18th to the beginning of the 19th centuries, in which persons not possessing a formal right to Imperial power usurped it
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Patronage of Art (entry)
PATRONAGE OF ART is disinterested financial and other forms of participation in the culture, science, and assistance to figures of science and culture. The beginning for patronage of art in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pavel (Paul) I (1754-1801), Emperor
PAVEL (PAUL) I (1754, St. Petersburg - 1801), Emperor (from 1796). Son of Emperor Peter III and Catherine II. His first wife was Augusta Wilhelmina Princess of Hesse-Darmstadt (Natalia Alexeevna upon conversion to Orthodoxy) (1755-76); his second
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pavlovsk, Palace and Park Ensemble
PAVLOVSK, the palace and park ensemble in the town Pavlovsk, is one of the biggest landscape parks in Europe. Its total area is 600 hectares. In 1777, the estate located here was presented by Empress Catherine II to her son Prince Pavel Pavlovich on
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pavlovsk, town
PAVLOVSK, a town (from 1796), municipal unit, and the centre of the Pavlovsky District on the Slavyanka River. Known as Slutsk in 1918-44. As of 2002, the population count was approximately 16,000 inhabitants
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
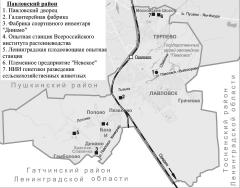
Pavlovsky District
PAVLOVSKY DISTRICT, an administrative and territorial unit of St. Petersburg, with its administration located in the town of Pushkin, at 24 Oktyabrsky Boulevard. It owes its name to the town of Pavlovsk at the district's centre
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Perovskaya S.L., (1853-1881), revolutionary
PEROVSKAYA Sofia Lvovna (1853, St. Petersburg - 1881), Revolutionary Populist. From the aristocratic noble family; father, Lev Nikolaevich Perovsky (1816-1890), was Petersburg Civil Governor in 1865-66
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Peter III (1728-1762), the Emperor
PETER III (1728-1762, Ropsha, St. Petersburg Province), Emperor (from 1761). Born Prince (from 1739, Duke) Karl Peter Ulrich von Holstein-Gottorp. Grandson of Emperor Peter the Great
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Petergofskaya Road
PETERGOFSKAYA ROAD (Petergofskaya Pershpektiva), name of Narvskaya Road between St. Petersburg and Peterhof in the 18th century. The road ran along the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland in place of the present-day Staro-Petergofsky Avenue
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Petrov V. P. (1736-1799), poet
PETROV Vasily Petrovich (1736-1799) poet, translator, collegiate counsellor (1786). Graduated from the Slavonic-Greek-Latin Academy in Moscow (1760). He became popular owing to the Ode to a Carrousel - the poetic description of the knights' gala
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Petrovsky Island
PETROVSKY ISLAND situated between the Malaya Neva River, Malaya Nevka River, and Zhdanovka River separating it from Petrogradsky Island. It is 120 hectares in area, three kilometres long, and 600 metres wide
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Petrovsky Park
PETROVSKY PARK is located on Petrovsky Island, along the left bank of the Zhdanovka River. It is surrounded with Petrovsky Avenue. Landscape planning of the present-day park (the total area is approximately 6
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Potemkin G. A. (1739-1791), statesman
POTEMKIN (from 1775 Potemkin-Tavrichesky) Grigory Alexandrovich (1739-1791), Count (1774) and His Highness, Prince (1775), statesman and military officer, favourite of Empress Catherine II, her secret spouse (from 1774) and virtual co-ruler
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Public Education (entry)
PUBLIC EDUCATION. It was Peter the Great who laid the basis for public education in St. Petersburg placing the greatest emphasis on military and professional education with the Naval Academy founded in approximately 1715
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Publishing houses (entry)
PUBLISHING HOUSES. Publishing in St. Petersburg dates back to 1711, when Tsar Peter the Great ordered the St. Petersburg Printing House to be established. The first printed matter issued in St. Petersburg was Vedomosti newspaper
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Radishchev A.N. (1749-1802), writer
RADISHCHEV Alexander Nikolaevich (1749-1802, St. Petersburg), writer, court counsellor (1780). In 1762-66 he was educated in the Page Corps. For the next five years he studied at Leipzig University
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rathaus
RATHAUS, the supreme authority of municipal government, established in St. Petersburg in 1798 by order of emperor Paul I instead of the abolished bodies of local government instituted by Cities Letter of Grant of 1785
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rinaldi А. (1709-1794), architect
RINALDI Antonio (around 1709-1794), architect of Italian descent. Studied in Naples under L. Vanvitelli. From 1752 served under Hetman K.G. Razumovsky in Malorussia (Little Russia, otherwise known as Ukraine). Since 1754 resided in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rumyantsev Family
RUMYANTSEV FAMILY, a noble family (from 1743 a family of Counts), known since the late 14th century. Those most closely associated with St. Petersburg include Peter Alexandrovich Rumyantsev (1725-1796), Count (1743) and Field Marshal General (1775)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Russian National Library
RUSSIAN NATIONAL LIBRARY (RNB) (18 Sadovaya Street), the oldest state general public library of the country, a research centre in the field of bibliology, bibliography and library science
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rybatskoe, area
RYBATSKOE, an area to the south-east of St. Petersburg, on the left bank of the Neva River, between the Murzinka River and the Slavyanka River. In 1716, Rybnaya (Fish) settlement was founded there at the Peter the Great’s decree
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sadovaya Street, Malaya
SADOVAYA STREET, MALAYA, between Italyanskaya Street and Nevsky Prospect (the shortest street of St. Petersburg, its length is 179 metres). It was built in the second half of the 18th century
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sarti G. (1729-1802), composer
SARTI Giuseppe (1729-1802), Italian composer, bandmaster, teacher. Managed the Court Capella in Copenhagen from 1768 to 1775, then, from 1779 to 1784 held the office of bandmaster at the San Marco Cathedral in Venice
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
"Severnaya Palmyra"(North Palmyra)
"SEVERNAYA PALMYRA" (North Palmyra) is a poetic name of St. Petersburg that came into Russian literature in the second half of the 18th century. In the ancient times
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sewerage System
SEWERAGE SYSTEM, wastewater treatment facilities. In the first quarter of the 18th century as the city territory grew, it was drained, and the system for discharge of surface water was built in the shape of plank-secured ditches along the city
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Shrovetide carnivals
SHROVETIDE CARNIVALS, mass popular carnivals that took place in the 18th - early 20th centuries during Shrovetide. Along with the Easter carnivals, Shrovetide was the most pompous and crowded of all
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Shubin F. I. (1740-1805), sculptor
SHUBIN (Shubnoy till 1761) Fedot Ivanovich (1740-1805, St. Petersburg), a sculptor. He lived in St. Petersburg from 1759. He was a student in the Academy of Arts in 1761-67, a retainer thereof in Paris in 1767-70 and Rome in 1770-72
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Shuvalov I.I. (1727-1797), statesman
SHUVALOV Ivan Ivanovich (1727-1797, St Petersburg), count, statesman, Adjutant-General (1760), Chief Chamberlain. Member of the Conference of the Supreme Court
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Smolny Institute
SMOLNY INSTITUTE situated at 1 Smolny Passage, the first and most privileged institute for noble young ladies. Empress Catherine II ordered the foundation of the institute in 1764 as the private Society for the Education of Young Noble Ladies
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sofia
SOFIA, the historical name of the town of Pushkin to the south of Catherine Park, between Pavlovskoe Freeway and Krasnoselskoe Freeway. It was founded in 1785 by Empress Catherine II as a chief town of the district. In 1782-88, St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
St. Catherine’s Lutheran Church
ST. CATHERINE’S LUTHERAN CHURCH, located at 1 Bolshoy Avenue of Vasilievsky Island. An architectural monument of early Classicism. Designed for the Lutheran Community of Vasilievsky Island (established in 1728) by architect Y. M
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
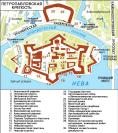
St. Peter and Paul fortress
ST. PETER AND PAUL FORTRESS, the historical centre of St. Petersburg, a monument of military engineering, the oldest engineering and architectural sight of the city
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
St. Petrischule
ST. PETRISCHULE situated at 10 Bolshaya Konyushennaya Street, a German school attached to St. Peter's Lutheran Church, the oldest school in St. Petersburg founded c. 1710. Scientist and teacher A. F
|
|
|
|
|