|
|
The subject index
/
February Revolution of 1917
February Revolution of 1917
Categories /
Social Life
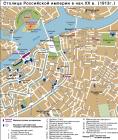
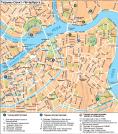
FEBRUARY REVOLUTION OF 1917 is the Second Russian Revolution, which dethroned the Monarchy. Decisive events developed in Petrograd. On 23 February (8 March) 1917, anti-military mass-meetings devoted to the Day of Women Workers began to grow spontaneously into strikes and demonstrations. The strike movement began in industrial factories on the Vyborgskaya Side (Torshilovskaya Factory, several plants including the Old Parviainen, the New Parviainen, the Lessner, and the Aivaz plants), then spread to other districts. On 23-24 February (8-9 March), separate groups of demonstrators penetrated the centre of Petrograd through the Liteiny and Troitsky bridges, and organized mass-meetings on Znamenskaya Square shouting the slogans "End the War!", "Down with Autocracy!", and "Bread!". Cossacks refused to act against the demonstrators. The commander of the Petrograd Military District, General S.S. Khabalov, gathered various reserve guards regiments at the city centre to enforce the security of bridges, governmental buildings and the telegraph system. On 25 February (10 March), a general strike started (approximately 305,000 workers from 421 industrial factories). On the evening of 25 February, Khabalov received a telegram from Emperor Nicolas II with a demand to halt the "disturbances" immediately. The troops were given an order to shoot at demonstrators. The police conducted mass arrests of members of different public organizations and left wing parties. On 26 February (11 March), bloody clashes occurred between demonstrators, police and troops; demonstrations were shot upon on Znamenskaya Square (40 killed and 40 wounded), at the corner of Nevsky Prospect and Sadovaya Street, and at the corner of the First Rozhdestvenskaya Street and Suvorovsky Avenue. The government's actions caused indignation and unrest among soldiers. During the second half of the day, the 4th Company of the Pavlovsky Reserve Regiment rebelled when soldiers opened fire on policemen; they were disarmed and arrested (their barracks were at 1 Konyushennaya Square; memorial plaque installed). On 27 February (12 March), an armed rebellion broke out in Petrograd. In the morning, soldiers from the Volynsky Regiment rebelled; they were followed by reserve soldiers from the Litovsky and Preobrazhensky regiments (their barracks were at 37/1 Kirochnaya Street; memorial plaque installed). On 27-28 February 1917, other units from the Petrograd Garrison joined them (on the morning of 27 February, 10,000 soldiers rebelled; during the course of the day, there were over 25,000; by evening, there were over 67,000; on 28 February, there were 127,000). The Main Arsenal, the Telegraph Service, the Central Post Office, and various railway stations, bridges, and governmental buildings all passed into the hands of revolting soldiers and workers. Police stations were looted; the Kresty (Crosses) Prison and the Temporary Confinement Building were captured; the Circuit Court buildings on Liteiny Avenue and the Lithuanian Prison Castle (on Kryukov Canal) were burnt; all prisoners were set free, and arrests began of the Tsar's ministers. General Khabalov and A. P. Balk, the Petrograd Chief of City Administration, together continued their resistance from the city administration building (2 Gorokhovaya Street), but to no avail. On 27 February, they sent a combined detachment headed by Colonel A. P. Kutepov with the purpose of "installing order", only to have the soldiers "disperse" among the rebels. Khabalov and all troops loyal to the government tried to consolidate at the building of the Main Admiralty, but by 28 February (13 March) 1917 the had to surrender. On 27 February (12 March), a new political organ of power was created at Tauride Palace, called the Provisional Committee of the State Duma (headed by M.V. Rodzyanko), which became the revolutionary forces' centre. At the same time, leaders from the State Duma's socialist factions, as well as representatives of soldiers and workers, all proclaimed the creation of a Temporary Executive Committee of the Petrograd Soviet of Workers' Deputies (from 1 (14) March, the Petrograd Soviet of Workers and Soldiers' Deputies). On 2 March (15 March), Emperor Nicolas II abdicated in Pskov in favour of his brother Prince Mikhail Alexandrovich, who on 3 March (16 March), in Petrograd at the apartment of Prince P.P. Putyatin (12 Millionnaya Street), refused to accept the highest power. On 2 March (15 March), the Provisional Government was formed (Prince G.E. Lvov became its head), receiving all governmental power and authority. The February Revolution was accompanied by numerous massacres and lynchings, murders of officers, particularly at the Kronstadt Rebellion on 1 (14) March. Over the course of the February Revolution, over 300 people were killed; on 23 March (5 April), 184 of those who had died were solemnly buried at the Field of Mars. In memory of the events of the February Revolution, Znamenskaya Square was renamed Vosstaniya Square (Uprising Square). A memorial plaque was erected on the facade of the Moskovsky Railway Station; a memorial plaque was also installed on the Crew Guards' barracks building at 22 Rimskogo-Korsakova Avenue. References: Бурджалов Э. Н. Вторая русская революция: Восстание в Петрограде. М., 1967; Старцев В. И. 27 февраля 1917. М., 1984; 1917 год в судьбах России и мира: Февр. революция: от новых источников к новому осмыслению. М., 1997. A. M. Kulegin.
Persons
Balk Alexander Pavlovich
Khabalov Sergey Semenovich
Kutepov Alexander Pavlovich
Lvov Georgy Evgenievich, Duke
Mikhail Alexandrovich, Grand Prince
Nicholas II, Emperor
Putyatin P.P., Duke
Rodzyanko Mikhail Vladimirovich
Addresses
1st Sovetskaya St./Saint Petersburg, city
Gorokhovaya St./Saint Petersburg, city, house 2
Kirochnaya St./Saint Petersburg, city, house 1/37
Konyushennaya Square/Saint Petersburg, city, house 1
Liteiny Ave/Saint Petersburg, city
Millionnaya St./Saint Petersburg, city, house 12
Nevsky prospect/Saint Petersburg, city
Rimsky-Korsakov Ave/Saint Petersburg, city, house 22
Sadovaya St./Saint Petersburg, city
Suvorovsky Ave/Saint Petersburg, city
The Field of Mars/Saint Petersburg, city
Vosstaniya Square/Saint Petersburg, city
Bibliographies
Бурджалов Э. Н. Вторая русская революция: Восстание в Петрограде. М., 1967
Старцев В. И. 27 февраля 1917. М., 1984
1917 год в судьбах России и мира: Февр. революция: от новых источников к новому осмыслению. М., 1997
The subject Index
Karl Marx Machine-Building Association (formerly Novy Lessner)
Pavlovsky Life Guards Regiment
Preobrazhensky Life Guards Regiment
Post Office, Central
Post Office, Central
Kresty Prison.
House of Preliminary Detention, prison
District Court
Lithuanian Castle.
Admiralty
Tauride Palace
State Duma
Petrograd Soviet of working people' and soldiers' deputies
Provisional Government of 1917
Field of Mars (Marsovo Pole), ensemble
Chronograph
1917
hidden
|
Alexandra Fedorovna, Empress (1872-1918)
ALEXANDRA FEDOROVNA (1872-1918), Empress (from 1894). Nee Victoria Alix Helena Brigitte Louise Beatrice, Princess of Hessen-Darmstadt. Wife of Emperor Nicholas II (from 1894)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Archive of Cinema, Photography and Audio Documents, St. Petersburg
ARCHIVE OF CINEMA, PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO DOCUMENTS, St. Petersburg (2 Muchnoy Lane) was founded in 1936 as Leningrad Regional Photo Archive, 1941-66 it was a part of the State Archive of the October Revolution and Leningrad Region Socialistic
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Archives, St. Petersburg
ARCHIVES, SAINT PETERSBURG, the Central State Archives of St. Petersburg situated at 15 Varfolomeevskaya Street. They were founded as the Leningrad Regional Archives of the October Revolution in 1936 and renamed as the State Archives of the October
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Balk A.P., the city guard 1916-17
BALK Alexander Pavlovich (1866-1957), statesman, Major General (1912). He graduated from the First Cadet Corps (he was a classmate of the future last minister of Internal Affairs of the Russian empire A. D
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bolshoy Dom
BOLSHOY DOM (Big House)(4 Liteiny Avenue), the name Leningraders gave to the administrative building where the bodies of Joint State Political Administration Board (OGPU), People's Commissariat of Home Affairs
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Brothel (entry)
BROTHEL (maison of tolerance), establishments where prostitutes provided sexual services for men. Secret houses of prostitution existed in St. Petersburg since the 18th century the first official public houses (brothels) appeared in 1843
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Capital
CAPITAL. St. Petersburg was the capital of Russia from the 1710s until 10-11 March 1918. The city's status as capital came quite spontaneously, and was mostly due to Tsar Peter the Great's having settled there
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Cemeteries (entry)
CEMETERIES. Even before the foundation of St. Petersburg there were several necropolises on the location of the future city: the records of the beginning of the 18th century indicate a Finnish-Swedish cemetery at Elagin (Aptekarsky) Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Central Duma
CENTRAL DUMA (Central City Duma) is the elected organ of city self-government. It was set up by the Provisional Government after the February revolution of 1917, dealing with the same problems as the previous City Duma
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Chaykovsky N.V. (1850-1926), revolutionary, political figure
CHAYKOVSKY Nikolay Vasilievich (1850-1926) was a political figure. On graduating from the 7th St. Petersburg Gymnasium (1868) he studied at the Faculty of Natural History of St. Petersburg University
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Chkheidze N.S. (1864-1926), a revolutionary, chairman of Petrograd Soviet in 1917
CHKHEIDZE Nikolay Semenovich (party pseudonym Carlo) (1864-1926), political figure. After graduating from Kutaisi gymnasia (1887) he entered Novorossiisk University (Odessa), but was soon expelled due to his participation in students' disorders
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
City Administration (entry)
CITY ADMINISTRATION. The system of City Administration in St. Petersburg from the beginning of the 18th century developed in 2 directions - the city government and self-government (see City self-government). From 1703 the city was governed by A. D
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
City Duma
CITY DUMA, administrative body of the city government. It was instituted in 1786 by Cities letter of grant (1785). City Duma was in charge of the city economy, taxes and levies, trade, medicine, education etc
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Constituent Assembly, All-Russian
ALL-RUSSIAN CONSTITUENT ASSEMBLY, a body of representatives established on the basis of universal suffrage in order to form a government and draft a Constitution for Russia
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Dan F. I. (1871-1947), Social Democrat, Menshevik
DAN (birth name Gurvich) Fedor Ilyich (1871, St. Petersburg - 1947), a statesman. On graduating from the Faculty of Medicine of Yuryev University (1895) Dan worked as a doctor of Obukhovskaya Hospital of St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
District Court
DISTRICT COURT, a judiciary body, established in the course of the Judiciary reform of 1864. Consisted of a chairman, his deputy and members of the court (appointed by the minister of Justice)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
District Soviets
DISTRICT SOVIETS, organs of state power on the territory of city districts in 1917-93. They appeared in the course of February revolution of 1917 as elected political organizations of workers and soldiers' deputies (17 District Soviets were formed
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Dubrovin A. I. (1855-1921), public figure
DUBROVIN Alexander Ivanovich (1855-1921) was a doctor, political and public figure, State Counsellor. On graduating from the Medical Surgical Academy (1879) he served as a military doctor. From 1889, he worked in children's orphanages of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ekaterinhof
EKATERINHOF, a country estate. Tsar Peter the Great presented it to his wife Ekaterina Alexeevna (the future Empress Catherine I) in 1711. It was situated on Ekaterinhofsky Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Factories and Plants' Committees
FACTORIES AND PLANTS' COMMITTEES, elected bodies of workers and employees' for self management. Emerged after the February Revolution of 1917, in contrast to trade unions
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Free Economic Society
FREE ECONOMIC SOCIETY, the Imperial Free Economic Society for the Encouragement of Farming and Housebuilding in Russia, the oldest Russian scientific society. It was founded in 1765 by large landowners striving for higher agricultural efficiency;
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Funeral Rites (entry)
FUNERAL RITES. Burials during the building of St. Petersburg were noted for their utmost simplicity. As C. Weber (1718) witnessed, "a body wrapped in a coarse bast sack, tightened with ropes, and put on a bier
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Head of the city administration
HEAD OF THE CITY ADMINISTRATION, the highest administrative and police rank in St. Petersburg. The post was introduced with the publication of the Regulations as of March 20, 1873 on St. Petersburg cessation from St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Highest Organs of State Power (entry)
HIGHEST ORGANS OF STATE POWER. The first higher organ of state power to function in St. Petersburg was the Senate founded by Tsar Peter the Great in 1711. The Supreme Privy Council was founded under Empress Catherine I (1725-30)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
His Imperial Majesty Personal Railway Regiment
The fist units of the Russian Railway Troops – the railway armed guards – were established in 1870; they were attached to railways. The total number of the Troops didn’t exceed 1000 people
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
House of Preliminary Detention, prison
HOUSE OF PRELIMINARY DETENTION (25 Shpalernaya Street), the first remand prison in Russia. It was built in 1871-75 (architect K.Y. Maevsky) who took American system as an example: the doors of cells overlooked stepped iron passages; inside the house
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Inter-Regional Party
INTER-REGIONAL PARTY (from the end of 1914 referred to as St. Petersburg Inter-Regional Committee of United Socialists Revolutionaries and Internationalists) was a socialist democratic organisation in St. Petersburg (Petrograd)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kerensky A.F. (1881-1970), political figure
KERENSKY Alexander Fedorovich (1881-1970), political figure and statesman, lawyer. In 1899, he entered the History and Philology Faculty of Petersburg University; in 1900, he moved to the Faculty of Law; after graduating (1904)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kodatsky I.F. the chairman of Leningrad Soviet in 1929-37
KODATSKY (Kadatsky) Ivan Fedorovich (1893-1937), Soviet statesman and party worker. He graduated from the vocational school in Nikolaev, worked as a turner there, took part in workers' strikes
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Komarov N.P. the chairman of Leningrad Soviet in 1926-28
KOMAROV Nikolay Pavlovich (born Fedor Evgenyevich Sobinov) (1886-1937), a statesman and Soviet Party worker. Had been living in St. Petersburg since 1902. In 1912 he graduated from the city 4-grade technical school
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kuzmin-Karavaev V.D. (1859-1927), public figure
KUZMIN-KARAVAEV Vladimir Dmitrievich (1859-1927) was a public and political figure, lawyer, publicist, Major General (1901). On graduating from the Corps of Pages (1878) he served in Guards' Mounted-Artillery Brigade
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lithuanian Castle.
LITHUANIAN CASTLE (Seven-towered castle), a prison, used to be situated in Kolomna, near the intersection of the Moyka river and Krukov canal. The 2-storeyed building of the palace was built in 1783-87 (architect I.E
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lopatin G.A. (1845-1918), revolutionary
LOPATIN German Alexandrovich (1845-1918, П.), revolutionary and narodnik (Russian populist). He graduated from the Department of Physics and Mathematics of St. Petersburg University (1866), in 1867, defended his Ph.D
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Markov II, N. E. (1866-1945), public and political figure
MARKOV Nikolay Evgenyevich (called Markov II in the State Duma, according to the seniority) (1866-1945) was a political and public figure, Collegiate Counsellor. He graduated from the Institute of Civil Engineers (1888)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
May Strikes ("Maevki").
MAY STRIKES ("Maevki"), secret gatherings of workers in the suburbs during pre-revolutionary Russia, in honour of the international workers solidarity celebration on 1 May, called May Day
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Merezhkovsky D.S. (1865-1941), writer and philosopher
MEREZHKOVSKY Dmitry Sergeevich (1865, St. Petersburg - 1941), a prose writer, poet, critic, literary and public figure. He graduated from Petersburg University with a major in philology in 1888. He married Z. N
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Military Industrial Committees
MILITARY INDUSTRIAL COMMITTEES (VPK), public administration for military and economic regulation, established during the First World War of 1914-18 for the mobilisation of private enterprises to producing military goods
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Milyukov P.N. (1859-1943), statesman, historian
MILYUKOV Pavel Nikolaevich (1859-1943), statesman, historian, essayist, honorary doctor of Cambridge University (1916). He graduated from the Faculty of History and Philology of Moscow University in 1882. From 1886, he was a private tutor there
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ministry of the Imperial Court
MINISTRY OF THE IMPERIAL COURT and Principalities (in 1852-56 The Ministry of the Imperial Court) was established in 1826 by request of the Emperor, the Imperial Family, and the Imperial Court
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Monarchical Organizations
MONARCHICAL ORGANISATIONS. The strengthening of liberal and radical opposition movements against absolutism provoked the appearance of monarchical organisations
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Morozov N.A. (1854-1946), revolutionary, chemist, astronomer
MOROZOV Nikolay Alexandrovich (1854-1946), revolutionary-narodnik, writer, scientist, author of memoirs, honorary member of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR (1932)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Myakotin V.A. (1867-1937), historian, public and political figure
MYAKOTIN Venedikt Alexandrovich (1867, Gatchina - 1937), historian, essayist, public and political figure. Graduated from Kronstadt Gymnasium and the Faculty of History and Philology of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Nicholas II, the Emperor (1868-1918)
Nicholas II (1868, Tsarskoe Selo - 1918), Emperor from 1894 to 1917. Son of Emperor Alexander III and Empress Maria Fedorovna. Married Princess of Hesse-Darmstadt, who took the name of Alexandra Fedorovna
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Panina S.V. (1871-1957), political figure
PANINA Sofia Vladimirovna, (1871, St. Petersburg - 1957), countess, educator and patron of the arts, political and public figure. Came from the family of Count Panin. Panina was one of the wealthiest women in Russia
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Petrograd Soviet of working people' and soldiers' deputies
PETROGRAD SOVIET OF WORKING PEOPLE' AND SOLDIERS' DEPUTIES (Petrograd Soviet), was established on February 27 (March 12 New Style), 1917 as Petrograd Soviet of working people's deputies; on March 1 (14 New Style) it united with Petrograd Soviet of
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Podvoysky N.I. (1880-1948), a revolutionist, statesman and military leader
PODVOYSKY Nikolay Ilyich (1880-1948), Soviet party worker and statesman. Graduated from the Demidov School of Law in Yaroslavl (1905). From 1907, he was in St Petersburg; in 1908, he was one of the leaders of the Zerno Bolshevik Publishing House
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Police
POLICE was created in St. Petersburg at the beginning of the 18th century; it was engaged in all the spheres of city life: construction, fire safety, city finances, public institutions, concert and theatre activities, etc
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Political Parties (entry)
POLITICAL PARTIES, groups of people united by political opinions and goals fixed in party documents; possessing certain membership requirements, internal structure and types of activities stated in the regulations; relying on a certain social base
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Prisons (entry)
PRISONS. The first prison in St. Petersburg (Convict gaol, or Convict yard, until 1732 under the jurisdiction of the Admiralty) was built in 1706 in the area of present-day Truda square
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Provisional Government of 1917
PROVISIONAL GOVERNMENT was the highest state organ of power in Russia, from 2 (15) March until 25 October (7 November) 1917. It was formed after the February Revolution of 1917 by the Provisional Committee of the State Duma in accordance with
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Public Safety Volunteer Units
PUBLIC SAFETY VOLUNTEER UNITS, arranged with the purpose of helping militia. Workers' units attached to industrial factories in the period of the Revolution of 1905-07 were a prototype of Public Safety Volunteer Units
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pushkin, town
PUSHKIN, a town and municipal unit situated south of Saint Petersburg. Known until 1918 as Tsarskoe Selo, and in 1918-37 as Detskoe Selo. As of 2002, population totalled approximately 95,000 inhabitants
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rasputin G. E. (1869-1916)
RASPUTIN Grigory Efimovich (1869-1916, Petrograd), religious preacher from a Siberian peasant family, spiritual tutor and close friend of the family of Emperor Nicholas II. In his religious views he was close to the so-called Khlysts
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Red Guards
RED GUARDS, the main organization of the working class' armed forces in Petrograd at the time of the 1917 Revolution and the first period of the Civil War. The first Red Guards detachments were created in Petrograd factories after the February
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Rodzyanko M.V. (1859-1924), political and public figure
RODZYANKO Mikhail Vladimirovich (1859-1924), public and political figure, author of memoirs. After graduating from the Page Corps in 1877, he served with the Mounted Regiment (transferred to the reserve in 1882, retired in 1885)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Security Department
SECURITY DEPARTMENT ("Security" in everyday language), the organ of police responsible for political search. It was created in 1866 as "The Department of Peace and Order in the Country" under the auspices of the Governor of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Shlyapnikov A.G. (1885-1937), political figure and statesman
SHLYAPNIKOV Alexander Gavrilovich (1885-1937), political figure. Graduated from a third-class professional training school and worked as a lathe turner. Lived in St. Petersburg from 1900
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
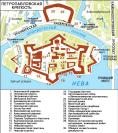
St. Peter and Paul fortress
ST. PETER AND PAUL FORTRESS, the historical centre of St. Petersburg, a monument of military engineering, the oldest engineering and architectural sight of the city
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Stalin I.V. (1878-1953), revolutionary, statesman
STALIN (real name Dzhugashvili) Iosif Vissarionovich (1879 (according to other sources, 1878) - 1953), Soviet statesman and party figure. Hero of Socialist Labour (1939), Hero of the Soviet Union (1945), Generalissimo of the Soviet Union (1945)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tarle E.V., (1874-1955), historian
TARLE Evgeny Viktorovich (1874-1955), historian, member of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR (1927). He graduated from the Faculty of History and Philology of Kiev University in 1896. In 1901, he moved to St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
The Russian Assembly , political organization
The RUSSIAN ASSEMBLY was a monarchical organization. It appeared in the beginning of October 1900 as a circle of top St. Petersburg officials and representatives of intelligentsia, adherents of the Russian style in life of the society. A.S
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Trade Unions (general article)
TRADE UNIONS, mass organisations that unite wage workers and salary workers to protect their economic rights and professional interests in the sphere of production, service and culture
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Trubetskoy Bastion
TRUBETSKOY BASTION, one of 6 bastions of Peter and Paul Fortress, situated in its south-western part. The bastion was built in 1703, of earth and wood under the supervision of prince Y.Y
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tsentralny (Central) District
TSENTRALNY (CENTRAL) DISTRICT, an administrative-territorial entity within St. Petersburg, with the territorial administration situated at 176 Nevsky Prospect. The district was set up in 1994, when Smolninsky District
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tsereteli I.G. (1881-1959), political figure
TSERETELI Irakly Georgievich (1881-1959), statesman, public and political figure. After graduating from Tiflis Gymnasium (1900) he entered the School of Law of Moscow University, in 1902
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tyrkova A.V. (1869-1962), the public and political figure
TYRKOVA (in marriage Williams) Ariadna Vladimirovna (1869, St. Petersburg - 1962) was a public and political figure, journalist, and writer. She studied at the Private Gymnasium of Princess A.A
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Union of Archangel Michael, the political organization
RUSSIAN NATIONAL UNION OF ARCHANGEL MICHAEL was a monarchical organization created by adherents of V. M. Purishkevich as a result of the split of the Union of the Russian People
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Uritsky M.S. (1873-1918), revolutionary, statesman
URITSKY Moisey Solomonovich (1873-1918, Petrograd), statesman. He graduated from the faculty of law of Kiev University (1897). After the split of Russian Social-Democratic Workers' Party (1903) he joined Mensheviks
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Vernadsky V.I., (1863-1945), chemist
VERNADSKY Vladimir Ivanovich (1863, St. Petersburg - 1945), chemist, mineralogist and crystallographer, Member of the Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1912), the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917), and the Academy of Sciences of the USSR (1925)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Victims of the Revolution, Monuments to the
VICTIMS OF THE REVOLUTION, MONUMENTS TO THE. The first monument To the fighters for the revolution was erected on the Field of Mars. On the 23 March (5 April, New Style) 1917, a ceremonial funeral took place here: 184 out of 1
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Vinaver M. M. (1863-1926), public figure
VINAVER Maxim Moiseevich (1862 or 1863-1926) was a public and political figure, and lawyer. On graduating from the Faculty of Law of Warsaw University (1886), he became an assistant to an attorney (from 1904 an attorney in St. Petersburg)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Voroshilov K.E. (1881-1969), statesman, marshal
VOROSHILOV Kliment Efremovich (1881-1969), Soviet statesman and military officer, Marshal of the Soviet Union (1935), Hero of the Soviet Union (1956, 1968), Hero of Socialist Labour (1960)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Vosstaniya Street
VOSSTANIYA STREET known as Znamenskaya (Holy Sign) Street until 1923, named after the Holy Sign Church. The street runs between Nevsky Prospect and Kirochnaya Street. The present-day name is in memory of the February Revolution of 1917
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Zarudny A.S. (1863-1934), lawyer, public and political figure
ZARUDNY Alexander Sergeevich (1863, St. Petersburg - 1934, Leningrad), public and political figure, lawyer. After graduating from the St. Petersburg Jurisprudence College in 1885, he worked at the St
|
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|