|
|
The subject index
/
Alexander Nevsky Lavra
Alexander Nevsky Lavra
Categories /
Architecture/Architectural Monuments/Architectural Ensembles
Categories /
Religion. Church/Monasteries and Convents
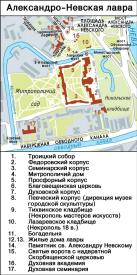
ALEXANDER NEVSKY LAVRA, located at 1 Alexander Nevsky Square. The monastery dedicated to the Holy Trinity and St. Alexander Nevsky. It was founded in 1710 by Tsar Peter the Great at the confluence of the Chernaya River (today the Monastyrka River) and the Neva River in memory of the victory of Prince Alexander Nevsky over Swedes in Neva battle of 1240. In 1797, the monastery received the status of Lavra. In 1712-13, the wooden Holy Annunciation Church and the monks’ cells were built. In 1715, construction of the entire building from brick started, supervised by architect D. Trezzini. By 1725, the eastern (Dukhovskoy) wing was completed and the garden was set out. In 1725-51, the North Wing was built (Feodorovsky; architects T. Schwertfeger, P. A. Trezzini), in 1756-58 - the West Wing was added (known as the Metropolitan Wing), in 1756-65 - the South Wing was completed (Seminary Wing). The Host Wing was completed in 1760-73 (all the wings were designed by architect M. D. Rastorguev). I. E. Starov completed the ensemble, building the Holy Trinity Cathedral, holy gates with Our Lady’s Church of Joy for All Who Sorrow (1783-85) and decorated the new square at the end of Nevsky Prospect. Lazarevskoe Cemetery (arranged in the beginning of the 18th century), Tikhvinskoe Cemetery (arranged in 1823) and Nikolskoe Cemetery (arranged in 1861) with their churches are situated on the territory of Alexander Nevsky Lavra (see Necropolis of the 18th century and Necropolis of Artists). In the necropolis of the Lavra many outstanding secular and church figures are buried. At the beginning of the 20th century there were 16 churches in Alexander Nevsky Lavra, it was a residence of the ruling Archpriest who was its superior. The Lavra was a centre of spiritual education. In 1720, a printing house was opened here. In 1726, a Slavonic-Greek-Latin Seminary was established, which became a foundation of the Theological Academy. In 1909, a Storehouse of Ancient and Unique Items was created. There was a rich library and an archive. On the eve of 1917, the Lavra finances reached three million roubles, with interest paying the expenses of Alexander Nevsky Orphanage and Isidorovskoe Eparchy School, with 130-150 students. Priests from the School were appointed to serve as naval priests. Subsidiary institutions belonging to the Lavra included Kinovia on the right bank of the Neva and Serafimo-Antonievsky hermitage on the river of Oredezh. In 1918, the Alexander Nevsky Lavra was closed, its archive, library and assets were nationalized. In 1923, monks were exiled, and in 1931-36, all the churches were closed. The premises of the Lavra housed different institutions, hostels and industrial facilities. In 1957, worship was recommenced in the Holy Trinity Cathedral. In 1994, the Alexander Nevsky Lavra was revived as a monastery and the residence of the Metropolitan. By 2000, all the buildings had been given back to the monastery. In 2002, on the square in front of the Lavra an equestrian monument to Alexander Nevsky was erected (sculptor V. G. Kozenyuk). The main religious holiday of the Lavra is 12 September, the day of transferral of the holy relics of St. Alexander Nevsky in 1724. References: Кудрявцев А. И., Шкода Г. Н. Александро-Невская лавра. Архит. ансамбль и памятники некрополей. Л., 1986; Антонов В. В., Кобак А. В. Святыни Санкт-Петербурга: Ист.-церков. энцикл. СПб., 1994. Т. 1. С.31-48; Рункевич С. Г. Свято-Троицкая Александро-Невская лавра (1713-1913): В 2 кн. СПб., 2001. V. V. Antonov.
Persons
Alexander Nevsky, Duke
Antonov Viktor Vasilievich
Kobak Alexander Valerievich
Kozenyuk Valentin Grigorievich
Peter I, Emperor
Rastorguev Mikhail Dmitrievich
Schwertfeger Theodor
Starov Ivan Egorovich
Trezzini Domenico
Trezzini Pietro Antonio
Addresses
Alexander Nevsky Square/Saint Petersburg, city, house 1
Bibliographies
Кудрявцев А. И., Шкода Г. Н. Александро-Невская лавра: Архит. ансамбль и памятники некрополей. Л., 1986
Рункевич С. Г. Свято-Троицкая Александро-Невская лавра (1713-1913): В 2 кн. СПб., 2001
Антонов В. В., Кобак А. В. Святыни Санкт-Петербурга: Ист.-церков. энцикл. СПб., 1994
The subject Index
Neva Battle (1240)
Lazarevskaya Burial Vault
Nikolskoe Cemetery
Necropolis of the18th Century
Necropolis of Artists
Theological Academy
Holy Trinity Cathedral of the Alexander Nevsky Lavra
Chronograph
1710
1717
1724
1790
1933
hidden
|
Alexander Nevsky, Prince (1220 or 1221-1263)
ALEXANDER NEVSKY (1220 or 1221-63), Prince of Novgorod (1236-51, not continously), of Tver (1247-52), Grand Prince of Kiev (1249-52) and Vladimir (1252-63), from the Rurikid Dynasty (11th generation), son of Yaroslav Vsevolodovich
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Alexandrovsky Parade Ground
ALEXANDROVSKY PARADE GROUND, the historical name of the territory in the south-west of the city center, around the Alexander Nevsky Lavra, north of Obvodnoy Canal and west of the Monastyrka River
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Alexy (Simansky), metropolitan in 1933-1945
ALEXY (born Sergey Vladimirovich Simansky) (1877-1970), religious figure, Doctor of Theology (1949). After graduating from the Faculty Of Law of Moscow University in 1899
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Anthony (Vadkovsky) (1846-1912), Metropolitan of St. Petersburg and Ladoga 1898-1912
ANTHONY (lay name Alexander Vasilievich Vadkovsky) (1846-1912, St. Petersburg ), Church figure, honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1899)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Belogradskaya E.T. (1739- after 1764), singer
BELOGRADSKAYA Elizaveta Timofeevna (1739, St. Petersburg - after 1764[?]), the first Russian singer (soprano) and harpsichord player. The daughter of lute player and singer Timofey Belogradsky
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bichurin N.Y. (Iakinf) (1777-1853), Chinologist, translator
BICHURIN Nikita Yakovlevich (monastic name Iakinf) (1777-1853, St. Petersburg), scholar of Eastern Studies, corresponding member of Russian Academy (1828). Graduated from the Theological Seminary of Kazan (1799)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Blagoveschenskaya (Holy Annunciation) Burial Vault
BLAGOVESCHENSKAYA (HOLY ANNUNCIATION) BURIAL VAULT (Holy Annunciation Burial Vault), the oldest stone chapel-monument of St. Petersburg, part of the Alexander Nevsky Lavra Ensemble
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Cabmen
CABMEN, appeared in St. Petersburg in the city's early days (decree of 1705 "On Taxing Cabmen"), at about the same time cab driving grew into a business practised as a rule by peasants. By 1745 there were 3,000 cabmen in St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Chichagov V.Y.(1728-1809) Admiral
CHICHAGOV Vasily Yakovlevich (1728-1809, St. Petersburg), Admiral. Graduated from the School of Mathematics and Navigational Sciences (1742), completed an internship in the British Navy, from 1745 served in the Baltic Fleet
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Church Press
CHURCH PRESS appeared in St. Petersburg after the organisation of the first printing presses, the first of which was established at the Alexander Nevsky Monastery in 1720
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Clerics of Novgorod and St. Petersburg (general article)
RULING CLERICS, members of the upper church hierarchy in the St. Petersburg Eparchy, consisting of bishops, archbishops and metropolitans. The Eparchy was known as the Eparchy of St. Petersburg and Schliesselburg (1742-70), St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Decembrists
DECEMBRISTS, members of secret societies, mainly, Guard officers and Masonic lodge members, who excited a rebellion against autocracy and serfdom in December 1825 (hence the name). Many of the future Decembrists were born in St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Dolgorukov Family
DOLGORUKOV (Dolgoruky), princely family, the Rurik Dinasty, important in the 15th century. Yakov Fedorovich Dolgorukov (1639-1720, St. Petersburg) was a statesman, associate of Peter the Great's, boyar (1697)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fountains (entry)
FOUNTAINS. The first fountains in St. Petersburg were laid out at the beginning of the 18th century in the Summer Garden. In 1717, the first engine was ordered (engineer Desaguliers) for their water supply and in 1717-1721 Ligovsky Canal was dug
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Frunzensky District
FRUNZENSKY DISTRICT, an administrative and territorial unit of St. Petersburg, with its administration located at 46 Prazhskaya Street. Formed in 1936, it was named in honour of Soviet statesman and military commander M. V
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Funeral Rites (entry)
FUNERAL RITES. Burials during the building of St. Petersburg were noted for their utmost simplicity. As C. Weber (1718) witnessed, "a body wrapped in a coarse bast sack, tightened with ropes, and put on a bier
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gavriil (Petrov) (1730-1801), Metropolitan of Nivgorod and St. Petersburg 1770-99
GAVRIIL (lay name Petr Petrovich Petrov-Shaposhnikov) (1730-1801), Church figure, honorary member (1776) and full member (1783) of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences. He graduated from the Slavonic-Greek-Latin Academy in Moscow (1754)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Goncharnaya Street
GONCHARNAYA STREET, from Vosstaniya Square to Poltavskaya Street. Known as Novaya Pershpektivnaya Road in the mid-18th century, assuming its present-day name in the 1780s after the potteries and potters' settlements that developed here
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gordeev F.G., (1744-1810), sculptor
Gordeev Fedor Gordeevich (1744, Tsarskoe Selo - 1810, St. Petersburg), sculptor. Studied at the Academy of Arts (1759-67) under N.F. Gillet, and received a retainer from the Academy of Arts to study in Paris (1767 - 1769) and in Rome (1769 - 1772)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Grigory (Chukov) (1870-1955), Metropolitan
GRIGORY (born Nikolay Kirillovich Chukov) (1870-1955), religious figure. After graduating from St. Petersburg Theological Academy in 1895, he took the post of the eparchial superintendent for theological schools of Olonets Eparchy
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Holy Trinity Cathedral of the Alexander Nevsky Lavra
HOLY TRINITY CATHEDRAL of the Alexander Nevsky Lavra, located at 1 Monastyrka River Embankment, is an architectural monument of the late Classicism style. Its location in the centre of the Lavra ensemble
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Ignaty (Bryanchaninov) (1807-1867), Orthodox Saint
IGNATY (born Dmitry Alexandrovich Bryanchaninov) (1807-1867), religious figure, theologian and spiritual writer. In 1822-26, he studied at the Central Engineering College of St. Petersburg, during this time he often visited the house A.N
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Isidor (Nikolsky) (1799-1892), Metropolitan of Novgorod and St. Petersburg 1860-1892
ISIDOR (born Iakov Sergeevich Nikolsky) (1799-1892, St. Petersburg), religious figure, honorary member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1857). After graduating from St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kazan Cathedral
KAZAN CATHEDRAL, Our Lady of Kazan Сathedral (2 Kazanskaya Square). A monument of Classical architecture. In 1733-1737, the three sided stone Church of the Nativity of the Virgin Mary, with a high bell tower, stood on this spot (architect M.G
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kupchino
KUPCHINO, a region of large scale residential housing in the south of St. Petersburg; it is confined in the north by Fuchika Street, in the east by the Moskovskaya Line of Oktyabrskaya Railway, in the west by a line of Vitebskaya Railway
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lamansky V.I., (1833-1914), Slavicist
LAMANSKY Vladimir Ivanovich (1833 - 1914, St. Petersburg), historian, philologist, member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1900). Graduated from the Faculty of History and Philology of the University of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lavrsky Bridges
LAVRSKY BRIDGES, two bridges over the Monastyrka River. Received their names from the Alexander Nevsky Lavra. The First Lavrsky Bridge is located in alignment with the main entrance to the Lavra
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lazarevskaya Burial Vault
LAZAREVSKAYA BURIAL VAULT, St. Lazarus’ Church within the ensemble of Alexander Nevsky Lavra. A small stone church (so-called tent) was built in 1717 behind the altar of the Holy Annunciation Church for the burial of Natalia Alexeevna (in 1723
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Leuchtenberg Family
LEUCHTENBERG (v. Leuchtenberg), a ducal family in Russia, its founder was Duke M. Leuchtenberg. In 1852, the Leuchtenbergs were included in the Imperial Family under the title of Princes Romanovsky. Initially they were buried at the SS
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Menageries (entry)
MENAGERIES. 1) In the beginning of the 18th century - hunting areas in the appendages of tsar's property. In 1718 a menagerie like that was established in Sarskaya farmstead (see Tsarskoe Selo)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Monasteries (entry)
MONASTERIES, there were four monasteries in Petrograd (two women’s convents and two men’s monasteries) by 1917, and 42 metochions, which functioned according to monastery regulations
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Monastyrka, river
MONASTYRKA, a river in the south-east of the central part of St. Petersburg, running from Obvodny Canal to the Neva River. The name originates from the monastery located on its banks, Alexander Nevsky Lavra
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Monastyrsky Island
MONASTYRSKY ISLAND situated between the Neva River, Obvodny Canal and Monastyrka River. It is 50 hectares in area, 900 metres long, and 600 metres wide. The island formed after Obvodny Canal was built in 1832
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Mordvinov S.I. (1701-1777), Admiral
MORDVINOV Semen Ivanovich (1701-1777, St. Petersburg), Admiral (1764). The father of N.S. Mordvinov. Studied in Novgorod and Narva Mathematical Schools, graduated from the Naval Academy in St. Petersburg (1716)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Museum of City Sculpture
MUSEUM OF CITY SCULPTURE, State Museum of City Sculpture (STCS) (179/2 Nevsky Prospect) was organised in 1939 with the aim to keep records, provide protection and carry out restoration of major monuments
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Naryshkin Family
NARYSHKIN FAMILY, a noble family, known since the 15th century, came to prominence after the marriage of Tsar Alexey Mikhailovich and Natalia Kirillovna Naryshkina, mother of Peter the Great, in 1671
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Necropolis of Artists
NECROPOLIS OF ARTISTS (in 1823-76, the New Lazarevskoe Cemetary; in 1876-1937, the Tikhvinskoe Cemetery). Memorial Necropolis Park included in 1937 in the City Sculpture Museum. Its square takes up 1.2 hectares
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Necropolis of the18th Century
NECROPOLIS OF THE 18TH CENTURY (before 1939, the Lazarevskoe Cemetery), memorial necropolis, part of the City Sculpture Museum (from 1932) on the territory of the Alexander Nevsky Lavra. Its square takes up 0.7 hectares
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Neva Battle (1240)
NEVA BATTLE (1240) is the name for the battle between Swedish forces and Russian retinue on the Neva River on 15 July 1240. The Swedes tried to capture the mouth of the Neva, Great Novgorod and Russia's only access to the Baltic Sea
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Nevskaya Zastava
NEVSKAYA ZASTAVA (outpost), a historical name of the territory along the left bank of the Neva River from Alexander Nevsky Lavra to Rybatskoe. It encompasses the following historical districts and localities: Steklyanny Settlement (Glass Settlement)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Nevsky Prospect
NEVSKY PROSPECT known as Bolshaya Pershpektivnaya Road or Bolshaya Pershpektiva until 1738, Nevskaya Prospektivaya Street or Nevskaya Perspektiva in 1738-1780s, and 25 October Avenue in 1918-44 so named in memory of the October Revolution of 1917
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
New Martyrs (entry)
NEW MARTYRS, representatives of the Orthodox clergy and laity, who died for their faith after the revolution. The title of the Protomartyr of St. Petersburg Eparchy was given to Archpriest Ioann Kochurov, Prior of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Nikolskoe Cemetery
NIKOLSKOE CEMETERY. One of the necropolises at the Alexander Nevsky Lavra, founded in 1863 (the third to be opened). Situated between Obukhovskoy Oborony Avenue and the Lavra's eastern yards. It was named after the Church of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Obnovlentsy
OBNOVLENTSY (RENOVATIONISTS), members of a reformatory movement in the Russian Orthodox church. In 1905, a "circle of 32 priests" was formed in St. Petersburg to initiate church reforms
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Obvodny Canal
OBVODNY CANAL flows from the Neva River in the area of Alexander Nevsky Lavra to the Ekaterinhofka River (8.08 km long, 21.3 meters wide and 42.6 meters wide in its eastern part)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Pallady (Raev) (1827-1898), Metropolitan of St. Petersburg and Ladoga in 1892-1898
PALLADY (born Pavel Ivanovich Raev-Pisarev) (1827-1898, St. Petersburg), religious figure, Honorary Member of St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1894). After graduating from Kazan Theological Academy (1852)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Peter the Great (1672-1725), Emperor
Peter the Great (Peter I) (b. 1672, d. 1725 in St. Petersburg), Tsar (from 1682) and Emperor (from 1721) of Russia, founder of St. Petersburg. Peter was the son of Tsar Alexey Mikhailovich (born from his second marriage) and N. K. Naryshkina
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Publishing houses (entry)
PUBLISHING HOUSES. Publishing in St. Petersburg dates back to 1711, when Tsar Peter the Great ordered the St. Petersburg Printing House to be established. The first printed matter issued in St. Petersburg was Vedomosti newspaper
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Saints of the St. Petersburg Eparchy (general article)
SAINTS OF THE ST. PETERSBURG EPARCHY, saints who lived on the territory of the Eparchy and were glorified by the Russian Orthodox Church. St. Prince Alexander Nevsky whose relics rest in Alexander Nevsky Lavra is a patron of the region and the city
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Serafim (Glagolevsky) (1757-1843), Metropolitan of Novgorod and St. Petersburg in 1821-1843
SERAFIM (born Stefan Vasilievich Glagolevsky) (1757-1843, St. Petersburg), religious figure, honorary member of St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1841). He studied at Moscow Theological Academy from 1782 and simultaneously attended lectures at
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Serafim Vyritsky (1866-1949), venerable
SERAFIM VYRITSKY (lay name Vasily Nikolaevich Muravyev) (1866-1949), a saint of the Russian Orthodox Church. In boyhood he moved to St. Petersburg where he worked in the Gostiny Dvor (merchant's court)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sheremetev Family
SHEREMETEV FAMILY, noble family, known since the 14th century (in 1706, the senior branch of the family was conferred the title of Counts). Several family members are closely connected with St. Petersburg
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Shishko L. P. (1872-1943), architect
SHISHKO Lev Petrovich (1872-1943, Lakhta settlement, by Leningrad), architect, teacher. Graduated from the Institute of Civil Engineering (1896). In the 1900s, was appointed architect to the Alexander Nevsky Lavra, built the New Vestry, a hotel
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Silvester (Kulyabka) (1701-1761), Archbishop of St. Petersburg in 1750-1761
SILVESTER (born Semen Petrovich Kulyabka, 1701, according to other evidence, 1704-61, St. Petersburg), religious figure. After graduating from Kiev Theological Academy (1726), he spent several years teaching there and in 1738 became its director
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sinopskaya Embankment
SINOPSKAYA EMBANKMENT, on the left bank of the Neva River, from Smolny Avenue to Alexandra Nevskogo Square. In the first half of the 18th century, it was called Naberezhnaya Street or Nevskaya Rozhdestvenskaya Embankment
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Sklyaev F. M. (1672-1728), shipbuilder
SKLYAEV Fedosey Moiseevich (1672-1728, St. Petersburg), shipbuilder, shipwright (1707), captain commander (1723). Sklyaev learned shipbuilding at Amsterdam's wharfs in 1697, in England in 1698, and in Venice in 1699
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
St. Isaac's Cathedral
ST. ISAAC'S CATHEDRAL, located at 1 St Isaac's Square, an architectural monument of late Classicism and the largest church in St. Petersburg. The first wooden church, which stood at the approximate location of the Bronze Horseman now
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
St. Petersburg Eparchy
ST. PETERSBURG EPARCHY, a territorial and administrative part of the Russian Orthodox Church. By decree of the Empress Elizaveta Petrovna the St. Petersburg Eparchy was separated from the Novgorod Eparchy on 1 September 1742. The bishop of St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Suvorov A.V.(1729-1800), military commander
SUVOROV Alexander Vasilyevich (1729-1800, St. Petersburg), military leader, Count of Rymnik (1789), Prince of Italy (1799), Generalissimo (1799). Received home education
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tchaikovsky P.I., (1840-1893), composer
TCHAIKOVSKY Peter Ilyich (1840-1893, St. Petersburg), composer, conductor, pedagogue, musical writer. Director of the Moscow branch of the Russian Musical Society (1885), member of the Paris Academy of Fine Arts
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
The Monument to Alexander Nevsky
This outstanding commander of the Ancient Rus, the greatest military leader of that time, the Grand Prince of Novgorod and Vladimir and his small army and Ladoga militia defeated the Swedish forces on July 15 (21), 1240
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Theological Academy
THEOLOGICAL ACADEMY located at 17 Obvodny Canal Embankment, closed higher theological education institution. It was founded under Metropolitan Gavriil in 1797 as the Alexander Nevsky Theological Academy based on the Main Seminary and situated in
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Trezzini D. (1670-1734), architect.
TREZZINI Domenico (circa 1670-1734), Italian of Swiss descent, architect, city-planner, representative of the Petrine Baroque (Peter's the Great epoch). From 1703, lived in Russia
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Trezzini Pietro Antonio (1692-1760s), architect
TREZZINI Pietro Antonio (1692-1760s), architect, representative of the Baroque style. A native of Italian Switzerland, studied in Milan. From 1726 lived in St. Petersburg, initially worked independently
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Tsentralny (Central) District
TSENTRALNY (CENTRAL) DISTRICT, an administrative-territorial entity within St. Petersburg, with the territorial administration situated at 176 Nevsky Prospect. The district was set up in 1994, when Smolninsky District
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Urban Plantations
URBAN PLANTATIONS, artificially created plantations: gardens, parks, forest parks, yards lawns, and the territory around ponds, squares, streets. The plantations perform the double function of sanitary protection and aesthetic city decoration
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Volkova Village
VOLKOVA VILLAGE, an area to the south of Obvodny Canal, between Moscow Line and Vitebsk Line of Oktyabrskaya Railway, on the banks of the Volkovka River. Since the early 16th century, there was a Novgorod settlement
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Vyshnegradsky I.A., (1831-1895), scientist technologist, businessman, statesman
VYSHNEGRADSKY Ivan Alexeevich (1831-95, St. Petersburg), statesman, scientist, businessman, Actual Privy Counsillor (1890), Honorary Member of Petersburg Academy of Sciences (1888)
|
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|
|