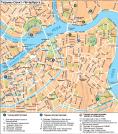
Addresses
/
Truda Square/Saint Petersburg, city
hidden
|
Admiralteyskaya Side
ADMIRALTEYSKAYA SIDE, a historical name of the central part of St. Petersburg bound on the north by the Neva river and on the south by the Moika River. Formed in the early 18th century when the General Admiralty
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralty Canal
ADMIRALTY CANAL was dug from the eastern ditch of the Amiralty Fortress (today, the Dvortsovy Bridge ramp to the Palace Square) to the Moika River to connect the Admiralty Shipyard with Galerny Dvor (Galley Yard) and warehouses of New Holland
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Efimov N.E. (1799-1851), architect.
EFIMOV Nikolay Efimovich (1799-1851, St. Petersburg), architect, urban planner. From 1806 to 1821, he studied at the St. Petersburg Academy of Fine Arts; was later involved in studying traditional Russian architecture. In 1827-40, he lived in Italy
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Fonvizin D.I. (1744/45-1792), writer
FONVIZIN (von Vizin) Denis Ivanovich (1744 or 1745 - 1792, St. Petersburg), writer, fellow of Russian Academy (1783). He was educated at a gymnasia attached to Moscow University (1755-62). His first visit to St. Petersburg dates back to 1759-60
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Galernaya Street
GALERNAYA STREET, runs from Dekabristov Square to Novo-Admiralteysky Canal Embankment crossing Truda Square. In 1738, it was known as Isaakievskaya Street (after St
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Holy Annunciation Church (Truda Square)
HOLY ANNUNCIATION CHURCH, on Truda Square, was erected for the Cavalry Life-Guards' Regiment in 1844-49 according to the designs of architect K. A. Ton and decorated in the Italian-Byzantine style
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Konnogvardeysky Boulevard
KONNOGVARDEYSKY BOULEVARD (in 1918-91, Profsoyuzov Boulevard), located between Dekabristov Square, St. Isaac's Square and Truda Square. The Admiralty Canal was excavated along Konnogvardeysky Boulevard in the early 18th century for transporting wood
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Kryukov Canal
KRYUKOV CANAL runs from the Admiralty Canal by Truda Square to the Fontanka River. 1015 meters long, it was dug from the Neva River to the Moika River in 1719-20 and was named after the contractor Semen Kyukov in 1738 (the section from the Neva to
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lieutenant Schmidt Bridge
LIEUTENANT SCHMIDT BRIDGE (in 1850-55 Blagoveshchensky, in 1855-1918 Nikolaevsky, in memory of Emperor Nicholas I). It was the first permanent bridge built over the Bolshaya Neva River, linking Truda Square (formerly Blagoveshchenskaya
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Prisons (entry)
PRISONS. The first prison in St. Petersburg (Convict gaol, or Convict yard, until 1732 under the jurisdiction of the Admiralty) was built in 1706 in the area of present-day Truda square
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Russian Style
RUSSIAN STYLE. A trend in Russian architecture of the 19th - beginning of the 20th century, based on using methods and shapes of ancient and traditional Russian art and architecture. The Russian style emerged out of the aesthetics of Romanticism
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Trolleybus
TROLLEYBUS, one of the principal means of the mass passenger city transport. The first tests of an electrical wire-operated car in Russia were conducted by engineer S.I. Schulenburg in 1902 in St. Petersburg at Froeze and C° plant
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Truda Square
TRUDA SQUARE, known as Blagoveshchenskaya Street from the 1830s to the 1880s, then called Blagoveshchenskaya Square until 1918. The square is surrounded by Angliiskaya Embankment, Konnogvardeysky Boulevard
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Yakubovicha Street
YAKUBOVICHA STREET, called Novo-Isaakievskaya Street until 1923, after St. Isaac's Cathedral, running between Isaakievskaya Square and Truda Square. The street was named after Decembrist A.I. Yakubovich (1792-1845)
|
|
|
|
|