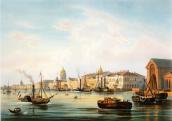Entries
/
hidden
|
Admiralteisky District
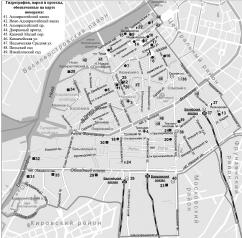
ADMIRALTEISKY DISTRICT, (Admiralty) an administrative territorial unit of St. Petersburg (Its territory administration is located at 10 Izmailovsky Avenue), is one of the central districts of the city
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Admiralteyskaya Side
ADMIRALTEYSKAYA SIDE, a historical name of the central part of St. Petersburg bound on the north by the Neva river and on the south by the Moika River. Formed in the early 18th century when the General Admiralty
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Angliiskaya Embankment
ANGLIISKAYA EMBANKMENT, from 1738 - Beregovaya Nizhnaya Embankment Street, in the mid-to-late 18th century - Isaakievskaya Embankment, Galernaya Embankment, and Anglinskaya Embankment, from 1800s - Angliiskaya Embankment
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Bolshaya Neva
BOLSHAYA NEVA, the largest left branch of the the Neva river delta; a continuation of the Neva River below the Dvortsovaya Bridge. The Bolshaya Neva flows into the Neva Bay of the Gulf of Finland, in the area surrounded by Vasilievsky Island
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Collot M.-A., (1748-1821), sculptor
COLLOT Marie-Anne (1748-1821), sculptor. Studied in Paris under E.M. Falconet. In 1766 she went together with him to St. Petersburg, becoming a member of the Academy of Arts in 1767. She sculpted marble busts of Prince G.G
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Dekabristov Square
DEKABRISTOV SQUARE (prior to 1925, also called Senatskaya, Petrovskaya), is situated between Admiralteyskaya Embankment and St. Isaac Square. It appeared at the beginning of the 18th century west of the outer bank of Admiralty Fortress;
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Falconet E. M., (1716-1791), sculptor
FALCONET Etienne Maurice (1716-1791), sculptor. He studied sculpture under J. B. Le Moin in Paris in 1734-44. He was the director of the Sevres Porcelain Factory in 1757-66
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Felten Y. M. (1730-1801), architect
FELTEN Yury Matveevich (Georg Friedrich) (1730 -1801, St. Petersburg), architect, professor of the Academy of Fine Arts (from 1775; from 1785 a Council member, in 1789-94 director), State Counsellor (1784)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Geological location
GEOLOGICAL LOCATION. St. Petersburg along with its outskirts is located on the convergence of two major tectonic structures: the southern Baltic Plate and the Northwest Russiаn Plate of the East European plain
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Gordeev F.G., (1744-1810), sculptor
Gordeev Fedor Gordeevich (1744, Tsarskoe Selo - 1810, St. Petersburg), sculptor. Studied at the Academy of Arts (1759-67) under N.F. Gillet, and received a retainer from the Academy of Arts to study in Paris (1767 - 1769) and in Rome (1769 - 1772)
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Lakhta, locality
LAKHTA, a landmark northwest of Saint Petersburg, on the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland, in the vicinity of a cognominal railway station and Lake Lakhta; neighbours Olgino on the West, and Staraya Derevnya on the East
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Peter the Great, Monuments to (entry)
PETER THE GREAT, MONUMENTS TO. Monument projects to Peter the Great in the capital founded by him appeared during his lifetime (particularly by N. Pinot, B. Tarsia). In 1716-20, B
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
St. Isaac's Cathedral
ST. ISAAC'S CATHEDRAL, located at 1 St Isaac's Square, an architectural monument of late Classicism and the largest church in St. Petersburg. The first wooden church, which stood at the approximate location of the Bronze Horseman now
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Symbols of St. Petersburg
THE SYMBOLS OF ST. PETERSBURG, works of art associated with St. Petersburg in the mass consciousness. The best known visual symbols include the weathercocks on the steeples of the SS
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
Thunder-stone
THUNDER-STONE, the name of the granite monolith, that serves as a pedestal to the equestrian statue of Emperor Peter the Great (see Bronze Horseman). It was discovered in 1768 in the forest near Konnaya Lakhta village by a local, S.G
|
|
|
|
|
|
hidden
|
|
hidden
|